
Examples of general business risks include the risk that a transaction will not occur or the obsolescence of a physical asset. If the U.S.-based company were able to do the currency exchange instantly at a constant exchange rate, there would be no need to deploy a hedge. Often, in such a scenario, a contract would be written which specifies the amount of yen to be paid and a date in the future for the yen to be paid. Since the U.S.-based company is unsure of the exchange rate on the future date, it may deploy a currency hedge with a derivative.
- With this relation the entity is offsetting the floating rate payments and will only pay the fixed rate.
- Due to market volatility, Company A is concerned that the fair value of its inventory might decline to $80,000.
- Companies are required to report the gains and losses on both the hedging instruments and the hedged items, distinguishing between the effective and ineffective portions.
- This assessment is forward-looking, focusing on expectations about future hedge effectiveness (IFRS 9.B6.4.12).
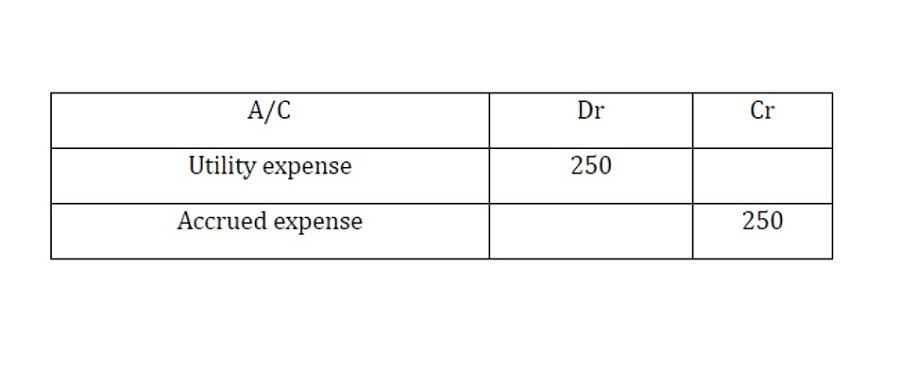
- This translates to an additional cash outflow of $100,000 that the company had not accounted for.
- This guarantees they will pay a set amount of USD in 90 days no matter what happens to currency markets in the interim.
- To qualify for hedge accounting, your business must formally document the relationship between the hedging instrument and the hedged item.
#2 – Cash Flow Hedge
These contracts allow parties to hedge risks or speculate on future price changes. Unlike IFRS 9, US GAAP does not allow an aggregated exposure to be designated as a hedged item because the items making up the aggregated exposure do not share the same risk exposure for which they are being hedged. Additionally, derivatives are not allowed to be designated as hedged items under US GAAP. Normal accounting does not require hedging instruments and items to have detailed documentation or pass a relationship effectiveness test.
Cash flow hedge example
A retrospective test is highly effective if the actual results of accounting the hedge are within the range 80%-125%. It does so by compensating for changes that are not reflective of an investment’s performance. The UK site includes all International content (see the separate listing by clicking the ‘International’ tab above), with PwC guidance tailored to the UK, as well as all of our UK GAAP content.
2 Introduction to hedge accounting
Foreign currency hedge accounting is grounded in the principle of matching the timing of gains and losses on hedging instruments with the underlying exposure they are intended to mitigate. This alignment ensures that the financial statements reflect the true economic impact of hedging activities, rather than presenting a distorted view due to timing mismatches. The goal is to provide a clearer picture hedge accounting of a company’s financial health and performance by smoothing out the volatility caused by exchange rate movements. Some common types of hedge accounting strategies include fair value hedge accounting, cash flow hedge accounting, and net investment hedge accounting in foreign operations.
Hedge Accounting Resources
Another significant reason that called for a change in the rules was its lack of matching concept. A user was unable to grasp an entity’s risk management activities of an entity based on the traditional way of accounting. The existing standard, IAS 39, was not pragmatic as it was not linked to standard risk management practices. The detailed rules had made the implementation of hedge accounting uneconomical, defeating the very purpose for which the same was created. However, the practice inherently brings on risk for the company, specifically the foreign exchange risk.

By easing some restrictions, IFRS 9 enables more hedging strategies to qualify for hedge accounting. In summary, hedge accounting is an important https://www.bookstime.com/articles/bookkeeping-for-shopify-sellers tool for managing risk while improving transparency in financial reporting. When used appropriately, it can help reveal a company’s true operating results.
- These requirements aim to enhance transparency around how companies use derivatives and manage risk.
- Readers will likely agree that hedge accounting can be a complex topic to grasp.
- The new standard which defines hedge accounting in a fresher perspective would reduce the time, effort, and expense of the businesses.
- Hedging instrument is a foreign currency forward contract to sell EUR for a fixed rate at a fixed date.
- Recording entries for hedge accounting is different from traditional accounting methods.
- The effective portion of the change in the value of the hedging instrument is recorded in OCI until the forecasted transaction affects the income statement.
2. Accounting for hedges

Unlike IFRS 9, a firm commitment to enter into a business combination or an anticipated business combination does not qualify as a hedged item under US GAAP. Companies that are exposed to market risks say foreign currency volatility, are more prone to incurring losses due to abrupt changes in the value of the currency they are dealing with. To hedge themselves, they use financial instruments, such as forward contracts, options, or futures as a part of their hedge accounting policy.

Criteria to qualify for hedge accounting
Hedge accounting is useful for companies with a significant market risk on their balance sheet; it can be an interest rate risk, a stock market risk, or most commonly, a foreign exchange risk. Also, the value of the hedging instruments moves according to movements in the market; thus, they can affect the income statement and earnings. Yet, hedge accounting treatment will mitigate the impact and more accurately portray the earnings and the performance of the hedging instruments and activities in the company in question. When testing effectiveness, IFRS 9 has moved away from bright lines and focuses on an objective-based test that requires an economic relationship of critical terms between the hedged item and the hedging instrument. Unlike IFRS 9, to qualify for hedge accounting under US GAAP, the hedging relationship must be highly effective – generally accepted to mean a range from 80% to 125% – which is more restrictive than IFRS 9.
This makes it easier for companies to apply hedge accounting for their risk management activities. Basis risk arises when the hedging instrument and the hedged item do not perfectly correlate, potentially weakening the hedge’s effectiveness. For instance, in commodity hedging, basis risk may occur if futures prices and spot prices diverge.
